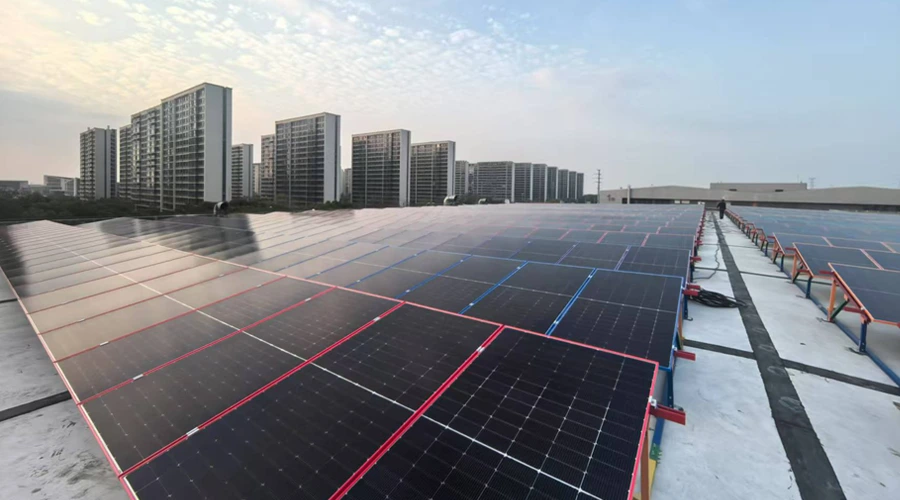
Composite material is already widely used in aerospace, automotive and wind blades because of its high strength, corrosion resistance, safe and harmless application as well as its high bending characteristics paired with its good insulation and long service life.
It consists of a composition of different raw materials such as glass fiber for mechanical strength, polyurethane as its matrix resin, a coating against UV aging, and felt for increased transverse strength.
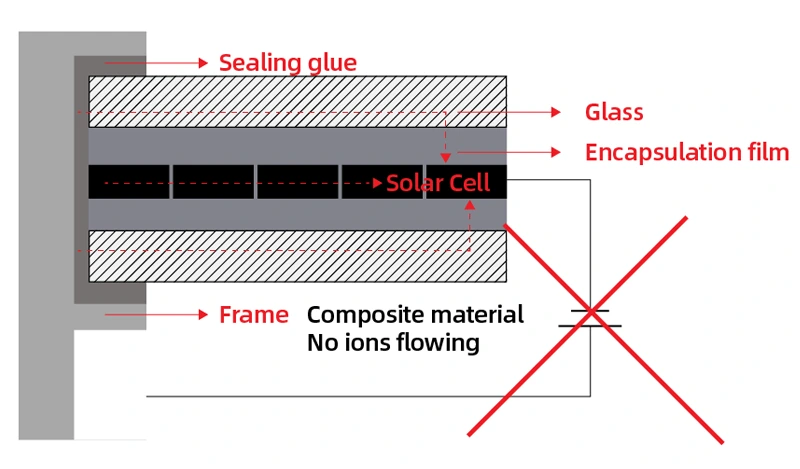
In PV panels, composite frame technology offers excellent mechanical and chemical properties enabling our solar modules to withstand higher loads and making them more resistant to harsh environmental conditions and increasing weather extremes. Thanks to their excellent insulation properties these frames effectively reduce PID. This is also due to the fact that no ions are flowing from the frame, which means no further grounding is required – reducing installation complexity and cost.
Our solar panels with composite frames have received a fire rating up to A level and are TUV, UL, REACH and ROHS compliant.